The FASB released an Accounting Standards Update on January 5, 2016 that changes items reported in OCI. Previously, equity securities could be classified as available for sale, and unrecognized gains and losses on these securities appeared in OCI. However, per this update, there is no longer an available for sale classification for equity securities if the fair value of these securities can be readily determined. Changes in the fair value of equity investments in unconsolidated entities flow through earnings for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017. This occurs when the cumulative unrealized losses exceed unrealized gains, indicating potential future expenses or losses. Understanding the line items within OCI allows investors and stakeholders to gain deeper insights into a company’s financial performance, risk exposure, and long-term sustainability.
Cash flow hedges aim to offset changes in cash flows of recognized assets, liabilities, or forecasted transactions. The effective portion of gains or losses on cash flow hedges is reported in OCI until the underlying hedged item impacts the income statement. First, it is essential to distinguish between realized gains and losses versus unrealized gains or losses. Understanding AOCI is essential for investors seeking to gain a more comprehensive perspective of a company’s financial health.
Conversely, unrealized gains represent the increase in value of an investment, asset, or security without a sale transaction. Corporate actions like hedging strategies or pension plan adjustments further contribute to AOCI fluctuations. For example, cash flow hedges employed to mitigate interest rate risks may shift AOCI as hedging instruments’ fair value changes. Similarly, actuarial gains or losses from pension plans, driven by changes in discount rates or demographic assumptions, add volatility to AOCI. Changes in the fair value of pension plan assets and actuarial gains or losses, such as changes in assumptions or demographics, impact the funded status of a pension plan. These adjustments are recognized in OCI, reflecting the potential impact on future pension obligations and the overall financial position of the company.
Understanding the Income Statement
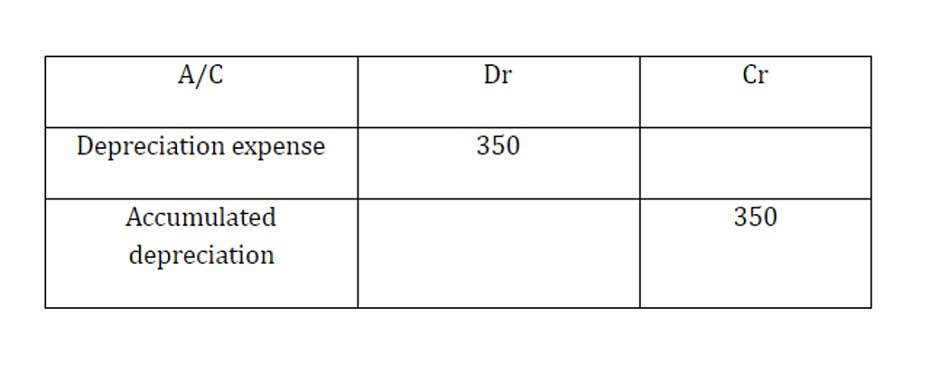
At the end of the income statement is net income; however, net income only recognizes incurred or earned income and expenses. Sometimes companies, especially large firms, realize gains or losses from fluctuations in the value of certain assets. The results of these events are captured on the cash flow statement; however, the net impact to earnings is found under “comprehensive” or “other comprehensive income” on the income statement. Accumulated other comprehensive income includes unrealized gains and losses reported in the equity section of the balance sheet.
- Analysts may calculate profitability and performance metrics using comprehensive income, which includes both net income and OCI.
- You’ll see it reported in the equity section of the company’s balance sheet, separate from retained earnings.
- For example, foreign currency translation adjustments and revaluation surpluses are recognized in equity under ASPE.
- The most common components include investment-related gains/losses, pension plan expenses, and foreign currency hedging transactions.
Understanding Credit Card Meaning: A Complete Guide
Foreign currency exposure is a significant risk that multinational corporations face when operating in an increasingly globalized economy. To mitigate the risk, companies engage in various hedging transactions, such as foreign currency forward contracts, options, and swaps. These financial instruments help to reduce the uncertainty of future cash inflows or outflows due to changes in exchange rates.
Is accumulated other comprehensive income part of retained earnings?
Accumulated other comprehensive income is part of the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet, while other comprehensive income and net income are part of the income statement. At the end of a reporting period, your company can sweep the balance of other comprehensive income into accumulated other comprehensive income and then reset the other comprehensive income to zero. When a transaction reflected in accumulated other comprehensive income completes, the gain or loss transfers to net income on the income statement.
In financial analysis, OCI provides additional information beyond net income that can improve evaluations of a company’s financial health. Analysts may calculate profitability and performance metrics using comprehensive income, which includes both net income and OCI. Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid. These items are considered comprehensive because they capture economic activity that impacts a company’s equity but do not reflect operational performance during a specific period. It’s calculated by adding or subtracting all recognized but unrealized incomes and losses from previous periods to current period totals. Items counted in AOCI could include changes in the value of available-for-sale securities, or how much foreign currency values have gone up or down.
- Accumulated other comprehensive income (OCI) includes unrealized gains and losses that are reported in the equity section of the balance sheet.
- AOCI provides insight into financial factors that impact equity but are not realized as cash income.
- When the functional currency of a subsidiary differs from the reporting currency of the parent company, fluctuations in exchange rates result in translation adjustments.
- So OCI provides valuable supplemental information on factors influencing financial performance beyond traditional profit and loss metrics.
- Accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) is a component of shareholders’ equity that reflects the cumulative effects of certain transactions and adjustments that are not included in net income.
- This happens because AOCI holds items that are not realized and hence don’t touch the profit or loss statement yet.
What does Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income include?
Accumulated other comprehensive income (OCI) includes unrealized gains and losses reported in the equity section of the balance sheet that are netted below-retained earnings. Other comprehensive income can consist of gains and losses on certain types of investments, pension plans, and hedging transactions. Bonds – When interest rates change, the fair market value of bonds can fluctuate, leading to unrealized gains or losses for bondholders.
It is analagous to retained earnings which is accumulating the revenues and expenses that are reported on each period’s income statement. By analyzing both components in combination, potential risks and opportunities can be identified more effectively. Imagine Company X’s investment portfolio includes stocks that have increased in value by $100,000 since purchase – these are unrealized gains. It also holds money in foreign currencies; due to exchange rate changes, it now has a $50,000 gain when converted back to U.S. dollars – this is another example of an unrealized gain that goes into AOCI. Accumulated other comprehensive income holds a unique position on the balance sheet, nestled within the equity section. It acts as a reservoir for certain gains and losses that, while not part of net income, must still be captured to represent a company’s total financial picture.
What is the difference between AOCI and retained earnings?
For instance, changes in interest rates affect the fair value of available-for-sale securities, leading to unrealized gains or losses in AOCI. A rise in rates could reduce the market value of a bond portfolio, resulting in a negative adjustment. Similarly, currency exchange rate movements influence foreign currency translation adjustments, especially for companies with substantial international operations. Pension plan expenses represent an essential aspect of accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI), accumulated other comprehensive income represents as they reflect unrealized gains and losses related to a company’s pension obligations.
Unrealized Gains and Losses on Derivative Instruments
Comprehensive income is the variation in a company’s net assets from non-owner sources during a specific period. Management uses AOCI to maintain transparency in financial reporting and to prepare for items that could transition from unrealized to realized gains or losses, impacting future earnings. Finally, subtract any comprehensive income items that have been reclassified to net income. While the calculation of AOCI can be somewhat complex, it is an important tool for investors who want to get a complete picture of a company’s financial performance. Unrealized foreign exchange gains or losses result when the fair value of the hedging instrument changes between the reporting dates. Conversely, if the euro weakens against the dollar, the company would record an unrealized loss.